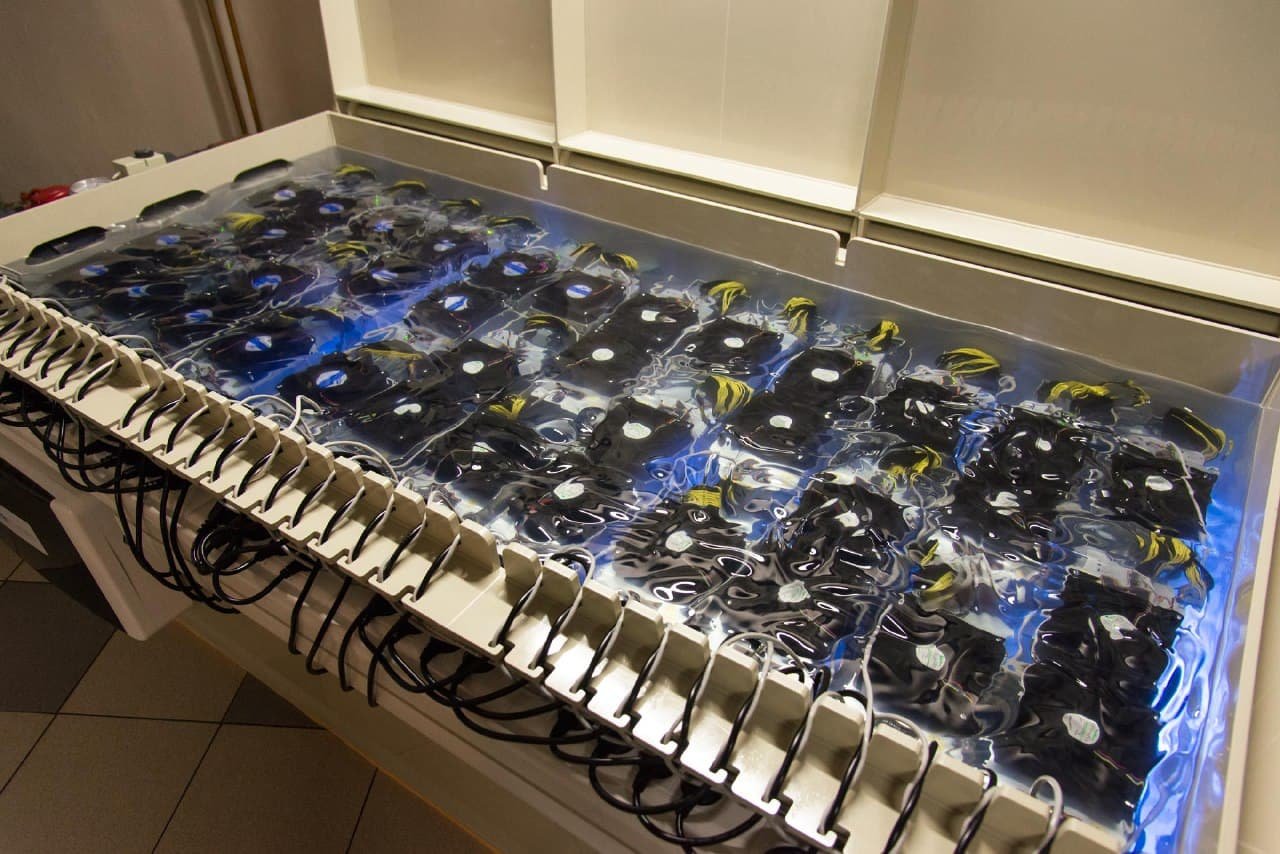
Importance of Liquid Cooling in Bitcoin Mining – Bitcoin mining has become an arms race where efficiency, performance, and sustainability dictate profitability. As miners strive to maximize returns while battling rising energy costs, hardware wear, and heat management challenges, liquid cooling emerges as a transformative solution.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Unlike traditional air cooling, which relies on fans and air circulation, liquid cooling delivers superior thermal regulation, enabling mining equipment to operate optimally under heavy workloads. Let’s dive deeper into the importance of liquid cooling in Bitcoin Mining, its advantages, and challenges, and why it’s increasingly being seen as the future of Bitcoin mining.
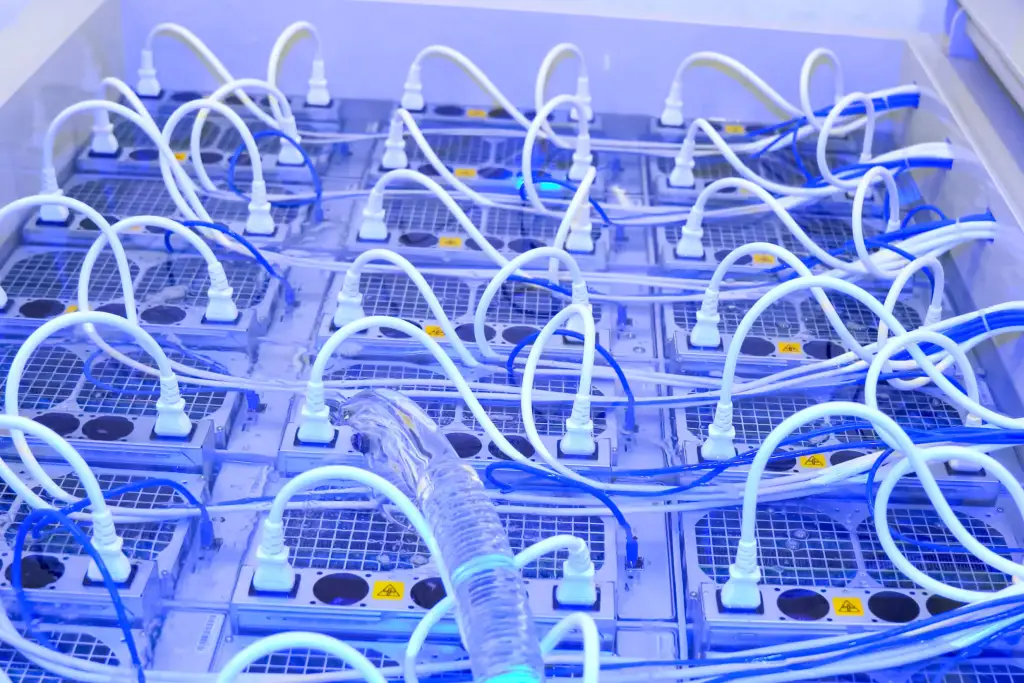

Why Liquid Cooling for Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin Mining includes a computational race to solve cryptographic puzzles, a process that is both power-intensive and generates considerable amount of heat. The ability to effectively dissipate this heat is crucial, not only for maintaining optimal performance but also for extending the lifespan of the mining hardware. Here’s why liquid cooling emerges as a vital technology in the context of Bitcoin mining:
Thermal Challenges in Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining, especially those equipped with powerful ASICs and GPUs, generate a significant amount of heat. If this heat isn’t managed properly, it can lead to thermal throttling where the hardware automatically slows down to prevent damage, or worse, it can cause permanent damage to the components. The challenge intensifies in densely packed mining setups or in climates that are naturally warmer, where traditional cooling methods struggle to maintain a safe operating temperature.
Benefits of Liquid Cooling in Bitcoin Mining
- Efficiency: Liquid cooling is far more efficient than air cooling due to the properties of the cooling medium. Liquids have a higher capacity to absorb and transfer heat compared to air. This superior heat transfer capability allows liquid cooling systems to quickly and efficiently remove heat from the core components of mining equipment, maintaining an optimal operating temperature and thus improving the overall hashing efficiency.
- Noise Reduction: Unlike air-cooled systems that rely on multiple high-speed fans, liquid cooling systems are significantly quieter. This reduction in noise is due to the reliance on water blocks and radiators that do not require fan cooling at high RPMs. For miners operating in residential areas or where noise could be an issue, liquid cooling offers a distinct advantage.
- Hardware Longevity: By maintaining lower temperatures, liquid cooling systems reduce the thermal stress on mining hardware, which can significantly extend the lifespan of the components. Cooler operating temperatures mean that electronic components such as GPUs and ASICs are less likely to suffer from heat-related wear and tear over time.
Core Components of Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid Cooling Systems are complex assemblies designed to manage heat more effectively than traditional air cooling. Each component plays a crucial role in the process, ensuring that mining equipment operate efficiently and reliably under optimal temperatures. Here’s an overview of each component and its function:
Coolants
Coolants are the lifeblood of any liquid cooling system. They are typically made from water or a glycol-water mixture but can also include more advanced fluids that enhance thermal conductivity and resist corrosion. The primary job of the coolant is to absorb heat from the mining components and transport it away to be dissipated.
Pumps
The pump is the heart of the liquid cooling system. It circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring continuous heat absorption from the mining hardware. A strong and reliable pump helps maintain consistent flow rates and pressures across all parts of the system, which is vital for effective cooling performance.
Radiators
Radiators act like the lungs of the cooling system. They are designed to dissipate the heat absorbed by the coolant into the surrounding environment. Radiators come in various sizes and thicknesses, with larger ones providing more surface are to aid in faster heat dissipation.
Water Blocks
Water blocks serve as the point of contact between the heat source and the coolant. They are attached directly to heat-generating components like CPUs, GPUs, or ASIC chips. Water blocks transfer the heat from these components into the coolant. The efficiency of a water block in absorbing heat is critical to the overall effectiveness of the cooling system.
Reservoirs
Reservoirs provide a storage space for extra coolant within the system. They are essential for maintaining the coolant volume necessary for optimal system performance. Reservoirs also allow for easier maintenance and filling of the coolant, and they help to eliminate air bubbles from the system, which can impede cooling performance.
Tubing
Tubing connects all components of the liquid cooling system, forming the channels through which the coolant flows. The quality and layout of the tubing affect the efficiency and aesthetic of the entire system. Flexible tubing is easier to install but may kink, reducing flow rates, while rigid tubing offers cleaner aesthetics and better flow but requires more precise installation.
These components work together to form a highly efficient system that maintains the mining hardware at optimal temperatures, thereby enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Each component’s design and quality can significantly affect the overall cooling efficiency, making it crucial to choose high-quality parts when setting up a liquid cooling system.
Setting Up Your Liquid Cooling System
Installing a liquid cooling system for Bitcoin mining requires meticulous planning and execution to ensure maximum efficiency and prevent any potential issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to set up a liquid cooling system tailored for the needs of Bitcoin miners, along with tips on selecting the right components and avoiding common installation pitfalls.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Component Selection: Before assembly, select the appropriate components based on your mining specifications. This includes choosing the right size and type of radiator, pump, coolant, water blocks, reservoir, and tubing.
- Preparing the Workspace: Ensure you have a clean, static-free workspace to assemble the components. Gather all tools and fittings needed for installation.
- Installing the Water Blocks: Attach the water blocks to the CPUs, GPUs, or ASIC miners. Ensure that the thermal paste is applied correctly for optimal heat transfer.
- Mounting the Radiator and Fans: Install the radiator in a position that allows for maximum air flow, typically at the top or side of the case. Attach the fans to the radiator, ensuring they are configured to push or pull air through the radiator fins effectively.
- Setting up the Pump and Reservoir: Install the pump and reservoir. The reservoir should be positioned above the pump to allow gravity to feed coolant into the pump inlet, reducing the risk of air locks.
- Connecting the Tubing: Cut the tubing to the required lengths and connect all components, ensuring secure and leak-free fittings. Use clamps or compression fittings to secure the connections.
- Filling and Priming the System: Fill the reservoir with coolant and turn on the pump to circulate the fluid through the system. Check for leaks during this initial fill. Once filled, let the system run to expel any air bubbles trapped in the loop.
- Final Checks and Testing: Once the system is filled and free of air, check all connections again for any potential leaks under operation. Monitor the system temperatures to ensure the cooling is effective.
- System Maintenance: Establish a routine maintenance schedule to check coolant levels, clear out any blockages, and ensure the system operates efficiently.
Choosing the Right Components
- Radiator Size: The size of the radiator should correspond to the heat output of your mining hardware. More powerful setups may require larger, or multiple radiators.
- Pump Strength: Ensure the pump is strong enough to circulate coolant through the entire system effectively, especially if using a complex loop with multiple components.
- Type of Coolant: Use a non-conductive coolant specifically designed for liquid cooling systems to prevent corrosion and algae growth.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Leakage: Always double-check all fittings and connections. Consider using a leak testing kit before filling the system with coolant.
- Inadequate Cooling: Underestimating the cooling requirement can lead to overheating. Ensure your system’s cooling capacity exceeds your mining hardware’s heat output.
- Air Locks: Improper filling can cause air locks in the pump and reduce cooling efficiency. Ensure the reservoir is above the pump and properly bleed the system.
By carefully following these steps, selecting the right components, and being aware of common pitfalls, you can effectively install and maintain a liquid cooling system that enhances the performance and longevity of your Bitcoin mining.
Conclusion
Liquid cooling systems offer significant advantages for Bitcoin mining operations, improving the efficiency, longevity, and overall performance of mining hardware. These systems efficiently manage the immense heat generated by mining activities, ensuring that hardware operates within optimal temperature ranges. This not only boosts the immediate operational capacity but also extends the life of the equipment by preventing overheating and associated damages.
For miners contemplating an upgrade from traditional air cooling to more advanced systems, liquid cooling offers a balanced approach. It provides superior cooling capabilities compared to air cooling and is generally less complex and costly than full-scale immersion cooling systems. Miners should assess their current and future scaling plans, budget constraints, and specific operational needs when deciding on the appropriate cooling technology.
Miners are encouraged to adopt sustainable and efficient cooling solutions to not only enhance the profitability of their operations but also reduce their environmental impact. By integrating advanced cooling technologies and considering potential reuse of waste heat, mining operations can become more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. This shift is not just beneficial for cost management but crucial for aligning with global sustainability goals.
FAQs on Importance of Liquid Cooling in Bitcoin Mining
Q1. What are the main challenges of Bitcoin mining?
A: The main challenges of Bitcoin mining include managing the significant heat generated by mining hardware, maintaining operational efficiency, and extending the lifespan of the expensive mining equipment.
Q2. Why is liquid cooling superior to air cooling for Bitcoin mining?
A: Liquid cooling is superior to air cooling because it is more efficient at transferring heat away from mining hardware, operates at lower noise levels, and can keep the mining setup cooler, thus improving the performance and longevity of the mining equipment.
Q3. What are the benefits of liquid cooling for mining?
A: The benefits of liquid cooling for mining include improved thermal efficiency, reduced noise, extended hardware longevity, and potentially lower energy consumption and operational costs compared to traditional air cooling methods.
Q4. How does immersion cooling differ from liquid cooling?
A: Immersion cooling differs from liquid cooling by submerging the entire mining equipment in a non-electrically conductive liquid, providing even more efficient heat removal and allowing for denser hardware configurations, albeit at higher setup complexities and costs.
Q5. What are the core components of a liquid cooling system?
A: The core components of a liquid cooling system include coolants, pumps, radiators, water blocks, reservoirs, and tubing, each playing a vital role in efficiently transferring heat away from the mining hardware.